Cold forming technology
Cold forming : Introduction
Cold forming is a manufacturing process that plastically deforms metal using dies. It allows for high speed production, little to no material waste compared to conventional machining, and creates a stronger end product due to work hardening of the material.
Basics of cold forming
*Header Machine (2-die, 3-blow)
STEP Material cut-off

Coil wire is cut into billets of a predetermined length.
STEP Forward extrusion

A processing method to reduce the diameter of a material by pushing it into a mold that is thinner than the material.
STEP Upset 1
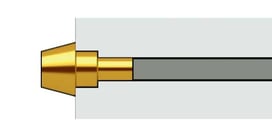
A processing method that utilizes perforated dies to facilitate material displacement. It is used to form shapes wider than the original material diameter.
STEP Upset 2
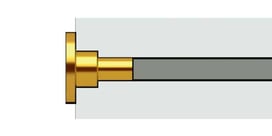
A processing method that utilizes perforated dies to facilitate material displacement. It is used to form shapes wider than the original material diameter.
STEP Backward extrusion
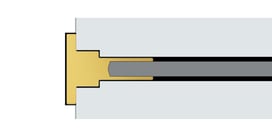
A processing method in which material is moved in the opposite direction of the force applied by the punch.
STEP Processing complete

The completed part is ejected from the last die
4 Advantages of cold forming

Advantage #1
High efficiency material utilization
(high yield)
The high material utilization of cold forging allows for significant reductions in material waste (scrap) compared to machining for the same geometry.

Advantage #2
Higher speed, more efficient production
Cold forming allows for high speed manufacturing (around 100 parts/minute) while still maintaining high precision and complex product geometries. No heating of the material is required.

Advantage #3
Improved product strength by work hardening
Cold forming process design takes fiber flow lines (the crystal structure of metals) into account allowing for stronger more durable parts.

Advantage #4
Cost reductions through customized manufacturing processes
If a customer design(tolerances, geometry, number of components required, etc) is practical using cold forming, significant improvements in part unit cost and reduced process complexity are possible.
Cold forming capabilities

We utilize over 1000 pieces of equipment in-house, including heading and rolling machines, deep drawing machines, and up to 8-stage parts forming machines. As a result, we ware able to produce complex shapes that are difficult to achieve normally through cold forming. In addition, our machines are equipped to handle a variety of raw materials, providing a high degree of flexibility in metal composition.
|
Range of forming machines |
1D2B~8D8B |
|---|---|
|
Wire diameter |
Φ 0.0039 in ~ Φ 0.9842 in |
|
Length |
0.0394 in ~ 47.24 in |
|
Control precision |
µin (㎛) |

Materials possible with cold forming
We have experience in processing the following materials with the cold forming process. If your preferred material is not listed below, please consult with us.
Product examples of cutom cold formed parts
We have many manufacturing achievements.